Maintainer: Manuel López-Ibáñez
Contributors: Manuel López-Ibáñez, Carlos M. Fonseca, Luís Paquete, and Mickaël Binois.
Introduction
This webpage documents the mooplot R package. There is also a mooplot Python package
The mooplot package implements various visualizations that are useful in multi-objective optimization. These visualizations include:
- Visualization of Pareto frontiers.
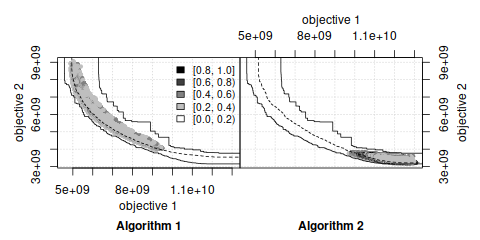
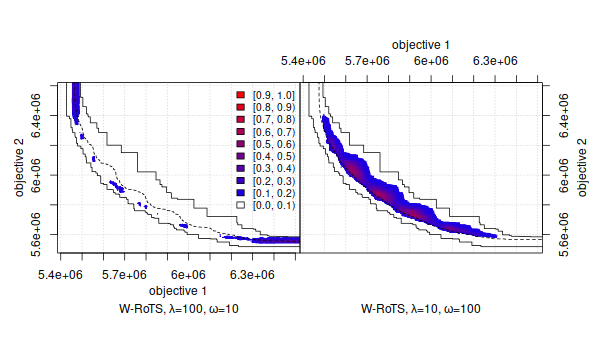
- Visualization of the Empirical Attainment Function (EAF) and the differences between EAFs. The EAF describes the probabilistic distribution of the outcomes obtained by a stochastic algorithm in the objective space.
These visualizations may be used for exploring the performance of stochastic local search algorithms for multi-objective optimization problems and help in identifying certain algorithmic behaviors in a graphical way.
The book chapter [1] explains the use of these visualization tools and illustrates them with examples arising from practice.
Keywords: empirical attainment function, summary attainment surfaces, EAF differences, multi-objective optimization, graphical analysis, visualization.
Relevant literature:
-
Manuel López-Ibáñez, Luís Paquete, and Thomas Stützle. Exploratory Analysis of Stochastic Local Search Algorithms in Biobjective Optimization. In T. Bartz-Beielstein, M. Chiarandini, L. Paquete, and M. Preuss, editors, Experimental Methods for the Analysis of Optimization Algorithms, pages 209–222. Springer, Berlin, Germany, 2010.
(This chapter is also available in a slightly extended form as Technical Report TR/IRIDIA/2009-015).
[ bibtex | doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-02538-9_9 | Presentation ]
Download and installation
The mooplot package is implemented in R. Therefore, a basic knowledge of R is recommended to make use of all features.
The first step before installing the mooplot package is to install R. Once R is installed in the system, there are two methods for installing the mooplot package:
-
Install within R (automatic download, internet connection required). Invoke R, then
install.packages("mooplot") -
Download the mooplot package from CRAN (you may also need to download and install all packages listed in
ImportsandSuggests), and invoke at the command-line:where
<package>is one of the three versions available:.tar.gz(Unix/BSD/GNU/Linux),.tgz(MacOS X), or.zip(Windows).
Search the R documentation if you need more help to install an R package on your system.
If you wish to be notified of bugfixes and new versions, please subscribe to the low-volume emo-list, where announcements will be made.
[ Download mooplot package from CRAN ] [ Documentation ] [ Development version (GitHub) ]
GitHub (Development version)
If you wish to try the development version, you can install it by executing the following command within the R console:
install.packages('moooplot', repos = c('https://multi-objective.r-universe.dev', 'https://cloud.r-project.org'))License
This software is Copyright (C) 2024 Manuel López-Ibáñez, Carlos M. Fonseca, Luís Paquete, Mickaël Binois.
This program is free software (software libre); you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Please be aware that the fact that this program is released as Free Software does not excuse you from scientific propriety, which obligates you to give appropriate credit! If you write a scientific paper describing research that made substantive use of this program, it is your obligation as a scientist to (a) mention the fashion in which this software was used in the Methods section; (b) mention the algorithm in the References section. The appropriate citation is:
- Manuel López-Ibáñez, Luís Paquete, and Thomas Stützle. Exploratory Analysis of Stochastic Local Search Algorithms in Biobjective Optimization. In T. Bartz-Beielstein, M. Chiarandini, L. Paquete, and M. Preuss, editors, Experimental Methods for the Analysis of Optimization Algorithms, pages 209–222. Springer, Berlin, Germany, 2010. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-02538-9_9
Moreover, as a personal note, I would appreciate it if you would email manuel.lopez-ibanez@manchester.ac.uk with citations of papers referencing this work so I can mention them to my funding agent and tenure committee.