This example illustrates how to sample random sets with mutually nondominated points.
Random nondominated sets in 2D
n <- 100
methods <- c("simplex", "concave-sphere", "convex-sphere", "convex-simplex")
colors <- c("red", "blue", "green", "purple")
shapes <- c(16, 15, 17, 18) # ggplot2 shape codes
df_all <- do.call(rbind.data.frame, lapply(methods, function(method) {
points <- moocore::generate_ndset(n, 2, method = method, seed = 42)
data.frame(x = points[,1L], y = points[,2L], method = method)
}))
ggplot(df_all, aes(x = x, y = y, color = method, shape = method)) +
geom_point(size = 2) +
scale_color_manual(values = colors) +
scale_shape_manual(values = shapes) +
theme_minimal() +
labs(x = expression(z[1]), y = expression(z[2]),
title = "Random Nondominated Sets (2D)")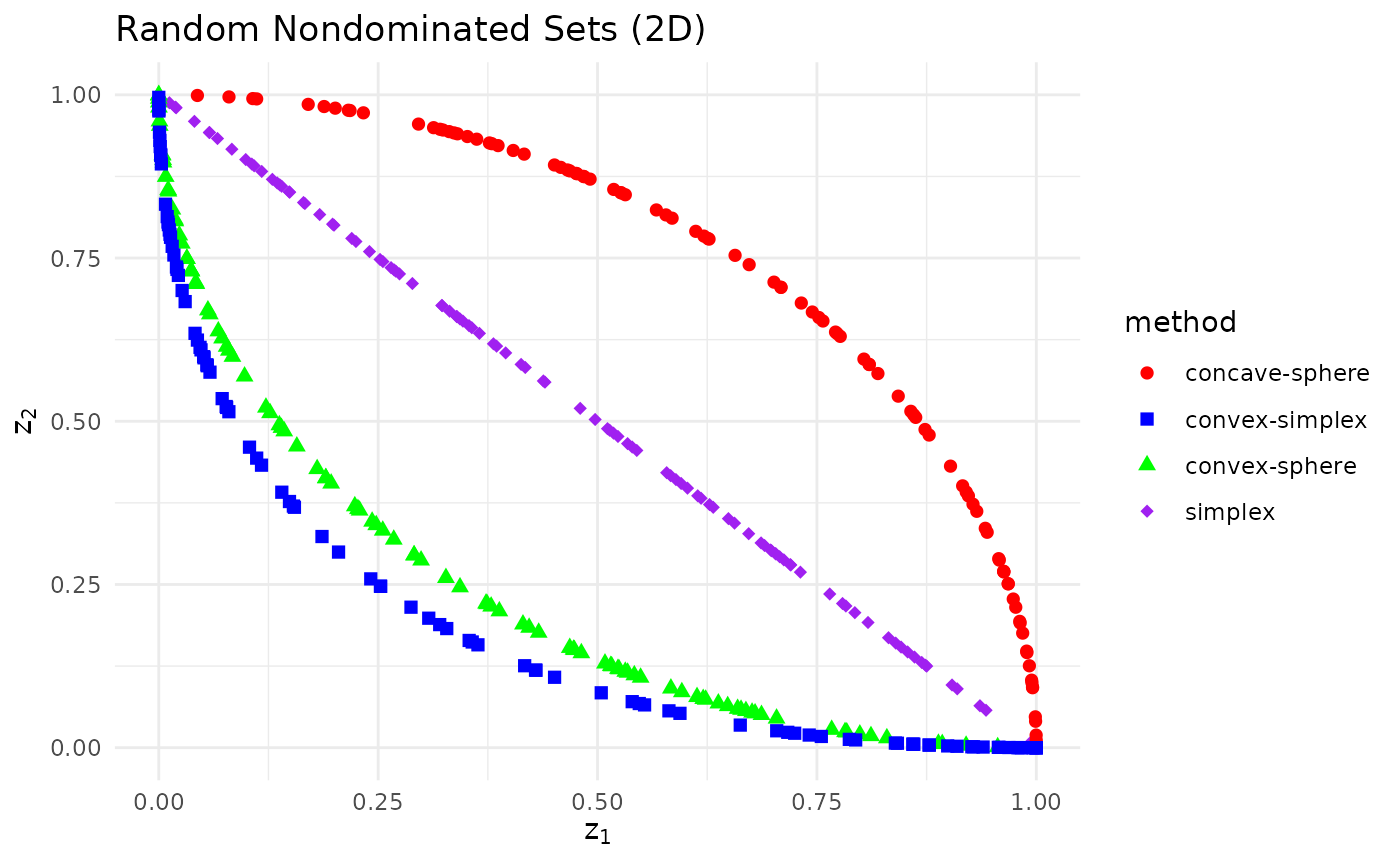
Random nondominated sets in integer space
We can also generate points in integer space.
points_list <- lapply(methods, function(method) {
moocore::generate_ndset(n, 2, method = method, seed = 42, integer = TRUE)
})
max_list <- sapply(points_list, max)
maximum <- max(max_list)
df_int <- do.call(rbind, lapply(seq_along(points_list), function(i) {
x <- points_list[[i]]
if (max_list[i] < maximum)
x <- moocore::normalise(x, lower = 0, upper = max_list[i], to_range = c(0, maximum))
data.frame(x = x[,1], y = x[,2], method = methods[i])
}))
ggplot(df_int, aes(x = x, y = y, color = method, shape = method)) +
geom_point(size = 2) +
scale_color_manual(values = colors) +
scale_shape_manual(values = shapes) +
theme_minimal() +
labs(x = expression(z[1]), y = expression(z[2]),
title = "Random Nondominated Sets in Integer Space (2D)")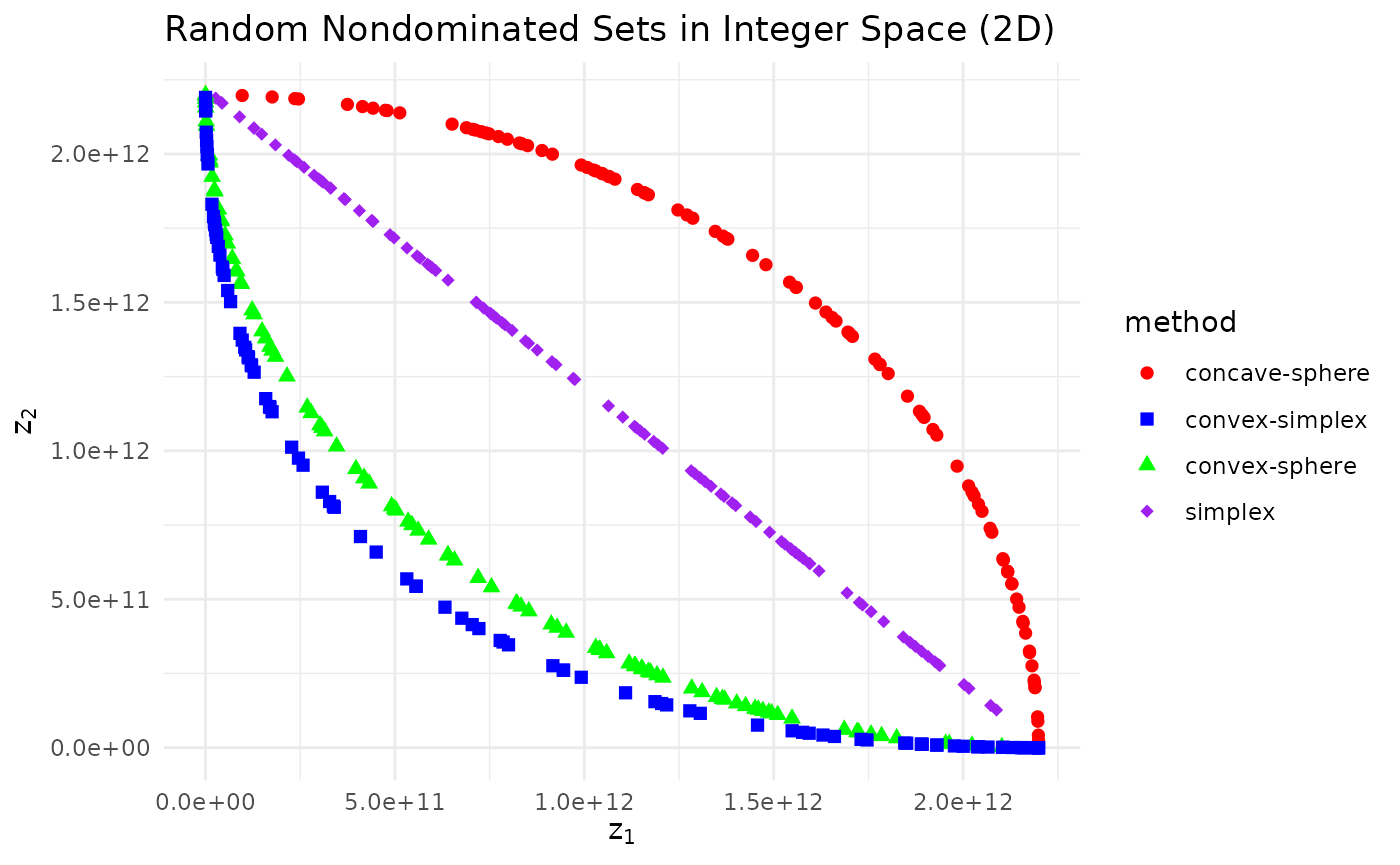
Variants of convex nondominated sets
A popular way to generate a convex nondominated set is to translate
the negative orthant of the hyper-sphere to the unit hyper-cube
(convex-sphere). However, there are other possible convex
sets with different properties. For example the method
convex-simplex applies a non-linear transformation to a
concave-sphere set, resulting in a convex transformation of
the standard simplex.
(show plotting code)
library(moocore)
library(htmltools)
library(plotly, warn.conflicts = FALSE)
plot_3d <- function(what, x, title) {
p <- plot_ly()
if (what == "simplex") {
# 2-simplex mesh
x_s <- diag(3)
p <- p %>% add_trace(
type = "mesh3d",
x = x_s[, 1L],
y = x_s[, 2L],
z = x_s[, 3L],
i = 0, j = 1, k = 2,
color = "cyan",
opacity = 0.2,
flatshading = TRUE,
name = "Simplex"
)
} else if (what %in% c("concave", "convex")) {
n_grid <- 50
phi <- seq(0, pi/2, length.out = n_grid)
theta <- seq(0, pi/2, length.out = n_grid)
grid <- expand.grid(phi = phi, theta = theta)
x_s <- matrix(sin(grid$phi) * cos(grid$theta), nrow = n_grid)
y_s <- matrix(sin(grid$phi) * sin(grid$theta), nrow = n_grid)
z_s <- matrix(cos(grid$phi), nrow = n_grid)
if (what == "convex") {
x_s <- 1 - x_s
y_s <- 1 - y_s
z_s <- 1 - z_s
}
p <- p %>% add_surface(
x = x_s,
y = y_s,
z = z_s,
colorscale = list(c(0, "cyan"), c(1, "cyan")),
opacity = 0.2,
showscale = FALSE
)
}
# Add scatter points
p <- p %>% add_trace(
type = "scatter3d",
mode = "markers",
x = x[, 1L],
y = x[, 2L],
z = x[, 3L],
marker = list(size = 2, color = "blue")
)
# Layout
p %>% layout(
title = title,
scene = list(
xaxis = list(title = "Z1", range = c(0,1)),
yaxis = list(title = "Z2", range = c(0,1)),
zaxis = list(title = "Z3", range = c(0,1)),
camera = list(eye = list(x = 1.2, y = 1.2, z = 0.8))
),
margin = list(l = 0, r = 0, b = 0, t = 40),
showlegend = FALSE
)
}
plotly_side_by_side <- function(fig1, fig2, height="500px") {
browsable(
tags$div(style="display:flex; justify-content: space-between;",
tags$div(style=sprintf("width:49%%; height:%s;", height),
plotly::as_widget(fig1)),
tags$div(style=sprintf("width:49%%; height:%s;", height),
plotly::as_widget(fig2))))
}
n <- 2000
points1 <- moocore::generate_ndset(n, 3, "convex-sphere", seed = 42)
fig1 <- plot_3d("simplex", points1, title = "Convex-sphere")
points2 <- moocore::generate_ndset(n, 3, "convex-simplex", seed = 42)
fig2 <- plot_3d("simplex", points2, title = "Convex-simplex")
plotly_side_by_side(fig1, fig2)Uniform sampling (moocore) vs projections of uniform samples (naive)
Naive methods for sampling such sets usually sample points uniformly in the hypercube and project them into a lower dimensional manifold (Lacour, Klamroth, and Fonseca 2017), e.g., the standard simplex or the positive orthant of the hypersphere. However, such projections do not preserve the uniformity of the sampling, that is, not all points in the manifold have the same probability of being sampled.
The function moocore::generate_ndset() produces a
uniform sampling on the manifold, as shown in the following
examples:
n <- 2000
# Simplex
points_moocore <- moocore::generate_ndset(n, 3, "simplex", seed = 42)
points_naive <- matrix(runif(n * 3), n, 3)
points_naive <- points_naive / rowSums(points_naive)
fig1 <- plot_3d("simplex", points_moocore, title = "Simplex (moocore)")
fig2 <- plot_3d("simplex", points_naive, title = "Simplex (naive)")
plotly_side_by_side(fig1, fig2)
# Concave-sphere
points_moocore <- moocore::generate_ndset(n, 3, "concave-sphere", seed = 42)
points_naive <- matrix(runif(n * 3), n, 3)
points_naive <- points_naive / sqrt(rowSums(points_naive^2))
fig1 <- plot_3d("concave", points_moocore, title = "Concave-sphere (moocore)")
fig2 <- plot_3d("concave", points_naive, title = "Concave-sphere (naive)")
plotly_side_by_side(fig1, fig2)
# Convex-sphere
points_moocore <- moocore::generate_ndset(n, 3, "convex-sphere", seed = 42)
points_naive <- 1 - points_naive
fig1 <- plot_3d("convex", points_moocore, title = "Convex-sphere (moocore)")
fig2 <- plot_3d("convex", points_naive, title = "Convex-sphere (naive)")
plotly_side_by_side(fig1, fig2)