Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Empirical Attainment Function#
This example illustrates functionality related to the EAF.
The AUC of the EAF and the AOC (Hypervolume)#
The Area-Over-the-Curve (i.e., the hypervolume) of a set of nondominated sets is exactly the Area-Under-the-Curve (AUC) of their corresponding EAF [14], as this example shows.
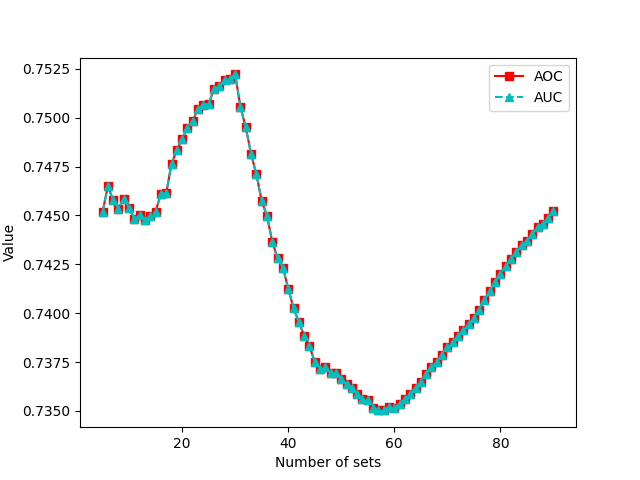
Runs = 90
AUC of EAF = 0.7452170740621844
Mean AOC = 0.7452170740621902
<Axes: xlabel='Number of sets', ylabel='Value'>
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import moocore
A = moocore.get_dataset("ALG_1_dat.xz")
sets = A[:, -1]
A = A[:, :-1]
A = moocore.normalise(A, to_range=[0, 1])
aoc = moocore.apply_within_sets(A, sets, moocore.hypervolume, ref=1)
aoc = aoc.mean()
eaf_a = moocore.eaf(A, sets=sets)
eaf_a[:, 2] /= 100
auc = moocore.hypervolume(eaf_a, ref=[1, 1, 0], maximise=[False, False, True])
nruns = len(np.unique(sets))
print(f"Runs = {nruns}\nAUC of EAF = {auc}\n Mean AOC = {aoc}\n")
runs = range(5, nruns + 1)
aocs = []
aucs = []
for r in runs:
selection = sets <= r
subsets = sets[selection]
a = A[selection, :]
aoc = moocore.apply_within_sets(
a, subsets, moocore.hypervolume, ref=1
).mean()
eaf_a = moocore.eaf(a, subsets)
eaf_a[:, 2] /= 100
auc = moocore.hypervolume(
eaf_a, ref=[1, 1, 0], maximise=[False, False, True]
)
aocs += [aoc]
aucs += [auc]
df = pd.DataFrame(dict(r=runs, AOC=aocs, AUC=aucs)).set_index("r")
df.plot(style=["rs-", "c^--"], xlabel="Number of sets", ylabel="Value")
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 2.917 seconds)