Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Comparing methods for approximating the hypervolume#
The following examples compare various ways of approximating the hypervolume of a nondominated set.
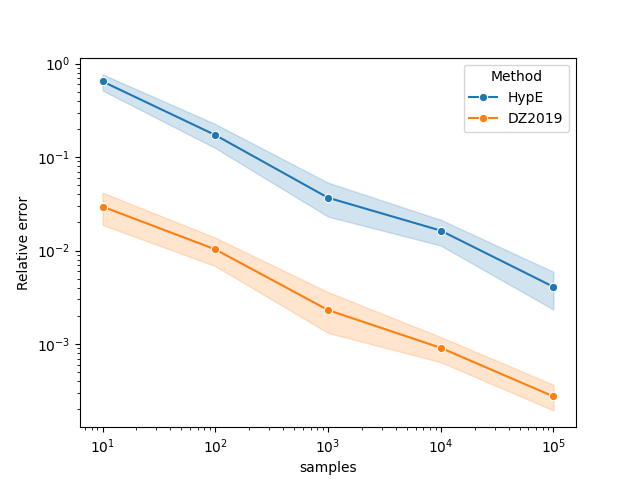
Comparing HypE and DZ2019#
This example shows how to approximate the hypervolume metric of the
CPFs.txt dataset using both moocore.whv_hype() (HypE), and
moocore.hv_approx() (DZ2019) for several values of the number of
samples between \(10^1\) and \(10^5\). We repeat each calculation 10
times to account for stochasticity.
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import moocore
First calculate the exact hypervolume.
ref = 2.1
x = moocore.get_dataset("CPFs.txt.xz")[:, :-1]
x = moocore.filter_dominated(x)
x = moocore.normalise(x, to_range=[1, 2])
true_hv = moocore.hypervolume(x, ref=ref)
Next, we approximate the hypervolume using \(\{10^1, 10^2, \ldots, 10^5\}\) random samples to show the higher samples reduce the approximation error. Since the approximation is stochastic, we perform 10 repetitions of each computation.
nreps = 10
nsamples_exp = 5
rng1 = np.random.default_rng(42)
rng2 = np.random.default_rng(42)
results = {"HypE": {}, "DZ2019-HW": {}, "DZ2019-MC": {}}
for i in range(1, nsamples_exp + 1):
for what in results.keys():
results[what][i] = []
res = moocore.hv_approx(x, ref=ref, nsamples=10**i, method="DZ2019-HW")
results["DZ2019-HW"][i].append(res)
for r in range(nreps):
res = moocore.whv_hype(x, ref=ref, ideal=0, nsamples=10**i, seed=rng1)
results["HypE"][i].append(res)
res = moocore.hv_approx(
x, ref=ref, nsamples=10**i, seed=rng2, method="DZ2019-MC"
)
results["DZ2019-MC"][i].append(res)
width = len("Mean DZ2019-MC")
text = "True HV"
print(f"{text:>{width}} : {true_hv:.5f}")
for what in results.keys():
res = results[what][nsamples_exp]
text = "Mean " + what
print(
f"{text:>{width}} : {np.mean(res):.5f} [{np.min(res):.5f}, {np.max(res):.5f}]"
)
True HV : 1.05704
Mean HypE : 1.05398 [1.04799, 1.05831]
Mean DZ2019-HW : 1.05704 [1.05704, 1.05704]
Mean DZ2019-MC : 1.05722 [1.05644, 1.05772]
Next, we plot the results.
df = [
pd.DataFrame(results[what]).assign(Method=what) for what in results.keys()
]
df = (
pd.concat(df)
.reset_index(names="rep")
.melt(id_vars=["rep", "Method"], var_name="samples")
)
df["samples"] = 10 ** df["samples"]
df["value"] = np.abs(df["value"] - true_hv) / true_hv
ax = sns.lineplot(x="samples", y="value", hue="Method", data=df, marker="o")
ax.set(xscale="log", yscale="log", ylabel="Relative error")
plt.show()
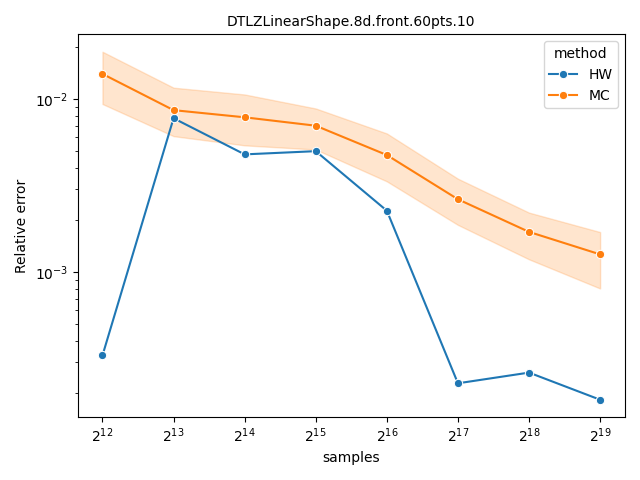
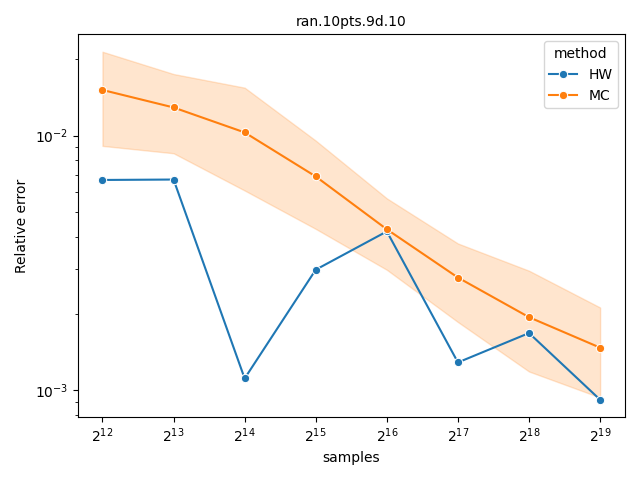
Comparing Monte-Carlo and quasi-Monte-Carlo approximations#
The quasi-Monte-Carlo approximation with method=DZ2019-HW is
deterministic, but not monotonic on the number of samples. Nevertheless, it
tends to be better than the Monte-Carlo approximation generated with
method=DZ2019-MC, specially with large number of objectives.
datasets = ["DTLZLinearShape.8d.front.60pts.10", "ran.10pts.9d.10"]
ref = 10
samples = 2 ** np.arange(12, 20)
maxiter = samples.max()
for dataset in datasets:
x = moocore.get_dataset(dataset)[:, :-1]
x = moocore.filter_dominated(x)
exact = moocore.hypervolume(x, ref=ref)
res = []
for i in samples:
hv = moocore.hv_approx(x, ref=ref, nsamples=i, method="DZ2019-HW")
res.append(dict(samples=i, method="HW", hv=hv))
for k in range(16):
seed = k
for i in samples:
hv = moocore.hv_approx(
x, ref=ref, nsamples=i, method="DZ2019-MC", seed=seed
)
res.append(dict(samples=i, method="MC", hv=hv))
df = pd.DataFrame(res)
df["hverror"] = np.abs(1.0 - (df.hv / exact))
df["method"] = df["method"].astype("category")
plt.figure()
ax = sns.lineplot(
data=df, x="samples", y="hverror", hue="method", marker="o"
)
ax.set_title(f"{dataset}", fontsize=10)
ax.set(yscale="log", ylabel="Relative error")
ax.set_xscale("log", base=2)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 50.045 seconds)