whv_hype#
- moocore.whv_hype(data, /, *, ref, ideal, maximise=False, nsamples=100000, dist='uniform', seed=None, mu=None)[source]#
Approximation of the (weighted) hypervolume by Monte-Carlo sampling (2D only).
Return an estimation of the hypervolume of the space dominated by the input data following the procedure described by Auger et al.[1]. A weight distribution describing user preferences may be specified.
Warning
The current implementation only supports 2 objectives.
- Parameters:
data (ArrayLike) – Numpy array of numerical values, where each row gives the coordinates of a point in objective space. If the array is created from the
read_datasets()function, remove the last (set) column.ref (ArrayLike) – Reference point as a numpy array or list. Must have same length as the number of columns of the dataset.
ideal (ArrayLike) – Ideal point as a numpy array or list. Must have same length as the number of columns of the dataset.
maximise (bool | Sequence[bool], default:
False) – Whether the objectives must be maximised instead of minimised. Either a single boolean value that applies to all objectives or a list of booleans, with one value per objective. Also accepts a 1D numpy array with values 0 or 1 for each objective.nsamples (int, default:
100000) – Number of samples for Monte-Carlo sampling. Higher values give more accurate approximation of the true hypervolume but require more time.seed (int | np.random.Generator | None, default:
None) – Either an integer to seednumpy.random.default_rng(), Numpy default random number generator (RNG) or an instance of a Numpy-compatible RNG.Noneuses the equivalent of a random seed (seenumpy.random.default_rng()).dist (Literal[‘uniform’, ‘point’, ‘exponential’], default:
'uniform') –Weight distribution [1]. The ones currently supported are:
'uniform'corresponds to the default hypervolume (unweighted).
mushould beNone.'point'describes a goal in the objective space, where
mugives the coordinates of the goal (1d Numpy array). The resulting weight distribution is a multivariate normal distribution centred at the goal.'exponential'describes an exponential distribution with rate parameter
1/mu, i.e., \(\lambda = \frac{1}{\mu}\).
mu (float | ArrayLike | None, default:
None) – Parameter ofdist. See above for details.
- Returns:
float – A single numerical value, the weighted hypervolume.
See also
References
Examples
>>> moocore.hypervolume([[2, 2]], ref=4) 4.0 >>> moocore.whv_hype([[2, 2]], ref=4, ideal=1, seed=42) 3.99807 >>> moocore.hypervolume([[3, 1]], ref=4) 3.0 >>> moocore.whv_hype([[3, 1]], ref=4, ideal=1, seed=42) 3.00555 >>> moocore.whv_hype([[2, 2]], ref=4, ideal=1, dist="exponential", mu=0.2, seed=42) 1.14624 >>> moocore.whv_hype([[3, 1]], ref=4, ideal=1, dist="exponential", mu=0.2, seed=42) 1.66815 >>> moocore.whv_hype( ... [[2, 2]], ... ref=4, ... ideal=1, ... dist="point", ... mu=[2.9, 0.9], ... seed=42, ... ) 0.64485 >>> moocore.whv_hype( ... [[3, 1]], ... ref=4, ... ideal=1, ... dist="point", ... mu=[2.9, 0.9], ... seed=42, ... ) 4.03632
Gallery examples#
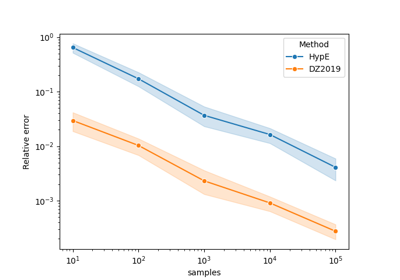
Comparing methods for approximating the hypervolume